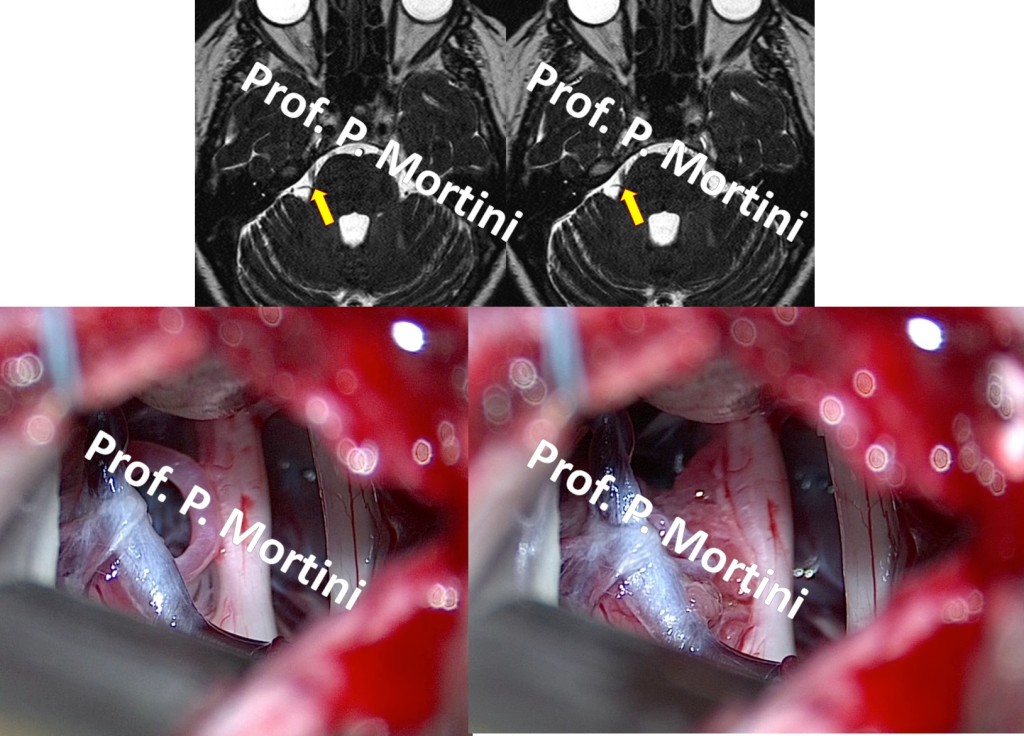
Microvascular Decompression (MVD) is a surgical treatment designed to treat facial pain or facial spasm that is refractory to medical therapies.
This microsurgical technique involves protecting important nerves, known as cranial nerves, with small Teflon sponges. In specific instances, small arteries and/or veins irritate these critical nerves by pushing on them. This anatomical relationship is often referred to as a “neurovascular conflict”.
Pressure on one or more nerves can cause severe pain as well as painful muscle spasms. MVD is most often used in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia, hemifacial spasm and glossopharyngeal neuralgia.
During MVD, surgeons separate the painful nerve from the offending vessel using a tiny Teflon sponge, thus relieving the pressure and allowing the nerve to heal.
MVD involves the use of general anesthesia and Microvascular Decompression surgery and is therefore not typically the first line of treatment.
However when the condition is extreme and/or more conservative care has been exhausted, this procedure can be extremely effective.
 English
English Italiano
Italiano